

Éducation internatioanle is mandated by the Ministère de l’Éducation du Québec to internationalize Quebec’s school service centres network and to coordinate the international promotion of vocational training in Quebec.

Éducation internatioanle is mandated by the Ministère de l’Éducation du Québec to internationalize Quebec’s school service centres network and to coordinate the international promotion of vocational training in Quebec.
![]()
Regulated by the Ministère de l’Éducation under the Government of Quebec

given in Canada’s two
official languages
French: +/- 85%
English: +/- 15%
![]()
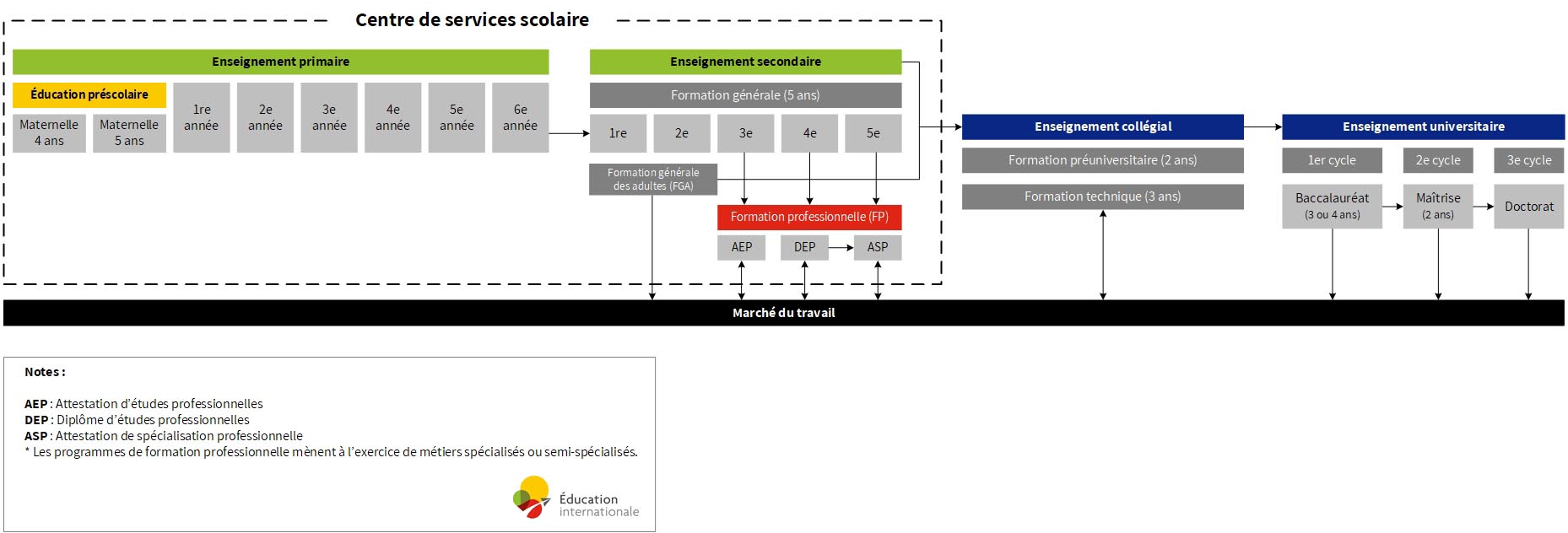
3 levels of education after
the general education:
Vocational training
College-level education
University-level education
SCHOOL SERVICE CENTRES AND SCHOOL BOARDS
Starting on June 15, 2020, the French-language school boards become school service centres governed by a board of directors.
In the English-language education system, the terms of office of the commissioners are maintained.
THEY ARE MANDATED BY THE GOVERNMENT TO MANAGE PUBLIC EDUCATION SERVICES, TO PROMOTE EDUCATION ON THEIR TERRITORY, AND ENSURE STUDENTS, YOUTHS AND ADULTS SUCCESS
Our members72
school service centres and school boards
60 French
9 English
3 special-status
2,370
Public schools
1 786 primary
393 secondary
191 primary-secondary
183
Adult education centres
187
Vocational training centres
1,200,000+
students
110,000+
teachers
4-5 years old
Preschool
(non-mandatory)
6-11 years old
Elementary | 6 years
Mandatory
12-17 years old
Secondary | 5 years
Mandatory until 16 years old
![]()
Education system among the world top 10
according to the OECD’s PISA
![]()
Competency-based approach (CBA)
That focuses on knowledge and skills assessed in the learning process
![]()
Ministry evaluation
during elementary and secondary education for the evaluation of learning to obtain certification
The province of Quebec is a world leader in vocational training. These short-term training programs (1 to 2 years) are geared toward learning a trade related to the job market.
Vocational training leads to a Diploma of Vocational Studies (DVS)
![]()
Learning through practice
80 % practice-based
20 % theory-based
![]()
Gears toward a specific field
through targeted learning and student internships
![]()
Competency-based education
that focus on the development of competencies rather than theoretical skills
![]()
Individual Education
guided/led by teachers to help students meet individual outcomes

144
Vocational training programs
Offered in 21 fields*
187
Vocation training centres
In Quebec
+ 115 000
students**
** Source: Annual report 2019-2020 of the Ministère de l’Éducation et de l’Enseignement supérieur of Quebec (MEES)
** Source: MEES, Portrait d’ensemble 2020-2021 des services et programmes d’études de la formation professionnelle
Want to learn more about vocation training?
Vocational training in Quebec Difference between vocational and technical training
Adult General Education (FGA) offers training activities (Literacy, francization, elementary and secondary education), as well as sociovocational Integrationthrough the acquisition of competencies for a semiskilled or unskilled occupation
FGA’s model and approaches are adapted to the needs of the learning communities in developing countries where Education internationale intervenes
![]()
Personalized learning to students
According to the acquired and desired competencies
![]()
Bridges to facilitate students’ transition
between FGA, vocational and technical training
![]()
Sociovocational Integration
of adult learners in collaboration with local community organizations
Higher education institutions cannot be member of our Cooperative. However, we collaborate with them in various projects and programs.
Public college education in Quebec is provided by CEGEPs, a French acronoym for collège d’enseignement general et professionnel.
Pre-University Program
2 years
general education + complementary component
Leads to a Diploma of College Studies (DCS)
Technical Program
3 years
general education + program-specific component based on skilled occupation or varied career fields
Difference between vocational and technical training

Universities provides undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate degrees. A doctoral degree can also lead to a post-doctoral studies.
Most universities also offer shorter programs leading to a certificate or a specialized graduate diploma (DESS).
Bachelor
3 or 4 years
Master
2 years
Doctorate
Research project